훈훈훈
Spring boot :: Caffeine cache 정리 본문
Introduction
사내에서 Local cache 라이브러리인 Caffeine cache 를 도입하게 되어 공부한 내용을 정리하게 되었다.
Caffeine cache 를 사용하면서 EhCache 와의 차이점이 궁금하여 두 라이브러리를 비교 후 간단한 예제 코드를 살펴보려고 한다.
예제 코드는 깃헙에서 확인할 수 있다.
Caffeine cache vs EhCache 3.xx
먼저 Caffeine cahce 에 대하여 살펴보자
Baeldung 에서는 Caffeine Cache 를 아래와 같이 소개하고 있다.

Caffeine 깃헙 위키는 아래와 같이 소개하고 있다.

공통적으로 High Performance Java caching Library 라고 소개하고 있다.
문서를 읽어보면 캐시와 ConcurrentMap 과의 차이점도 설명으로 덧붙이고 있다.
ConcurrentMap 에 저장된 데이터는 해당 Map 이 제거될 때까지 영구적으로 보관된다고 한다.
반면에 캐시는 evict 로직이 Auto 로 동작하게끔 구성이 된다고 한다.
그리고 Caffeine Cache 는 eviction policy 로 Window TinyLfu 라는 것을 사용한다.
해당 알고리즘을 사용함으로써 최적의 적중률(near-optimal hit rate)을 보여준다고 한다.
Window TinyLfu 에 대하여 궁금하다면 해당 링크를 읽어보길 바란다.
이제 Ehcache 에 대하여 살펴보자.
EhCache 는 Java 진영에서 유명한 Local Cache 라이브러리 종류 중 하나이다.
EhCache 는 Caffeine Cache 보다 더 많은 기능을 제공해준다.
분산 처리, Cache Listener 그리고 Off Heap 에 캐싱된 데이터를 저장할 수 있다. 그 외 더 많은 기능들은 공식문서에서 확인할 수 있다.
아래 그림은 Ehcache 공식문서에 있는 Distributed Caching 관련 내용이다.
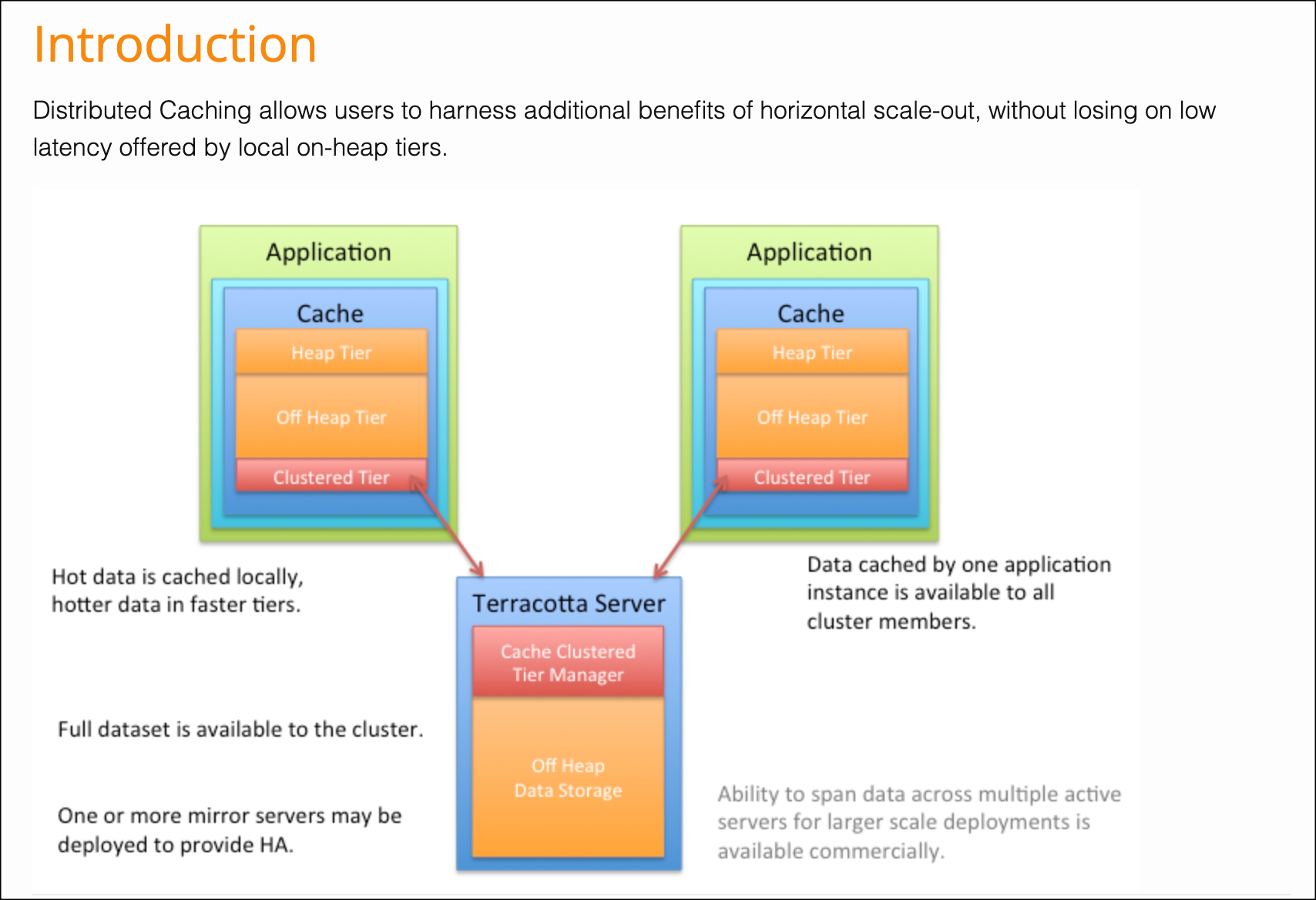
위 그림을 보면 각 어플리케이션 내에 저장되어 있는 캐시를 Terracotta 라는 Hub 역할을 하는 분산 캐시 서버에 동기화하는 과정을 볼 수 있다.
EhCache 의 Distributed Caching 에 대하여 좀 더 알아보고 싶다면 해당링크를 참고하길 바란다.
아래 그림은 EhCache 공식문서에 있는 Storage tiers hierarchy 구조이다.

EhCache 는 Heap 메모리 공간 이외에 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 Off Heap 기능을 지원한다.
Off Heap 기능을 사용하면 GC 로 부터 자유로워 질 수 있는 장점이 있다.
하지만, Off Heap 에 저장되어 있는 데이터를 저장 및 불러올 떄는 직렬화 비용이 발생하게 된다.
이제 벤치마크 자료를 통해 성능을 비교해보자.
아래 자료는 Caffeine cache 깃헙 위키에서 제공하는 데이터이다.
측정 값과 단위는 아래와 같다.
- Throughput: 단위 시간당 디지털 데이터 전송으로 처리하는 양
- ops/s: operations per second (초당 작업)
읽기 100% 성능 측정
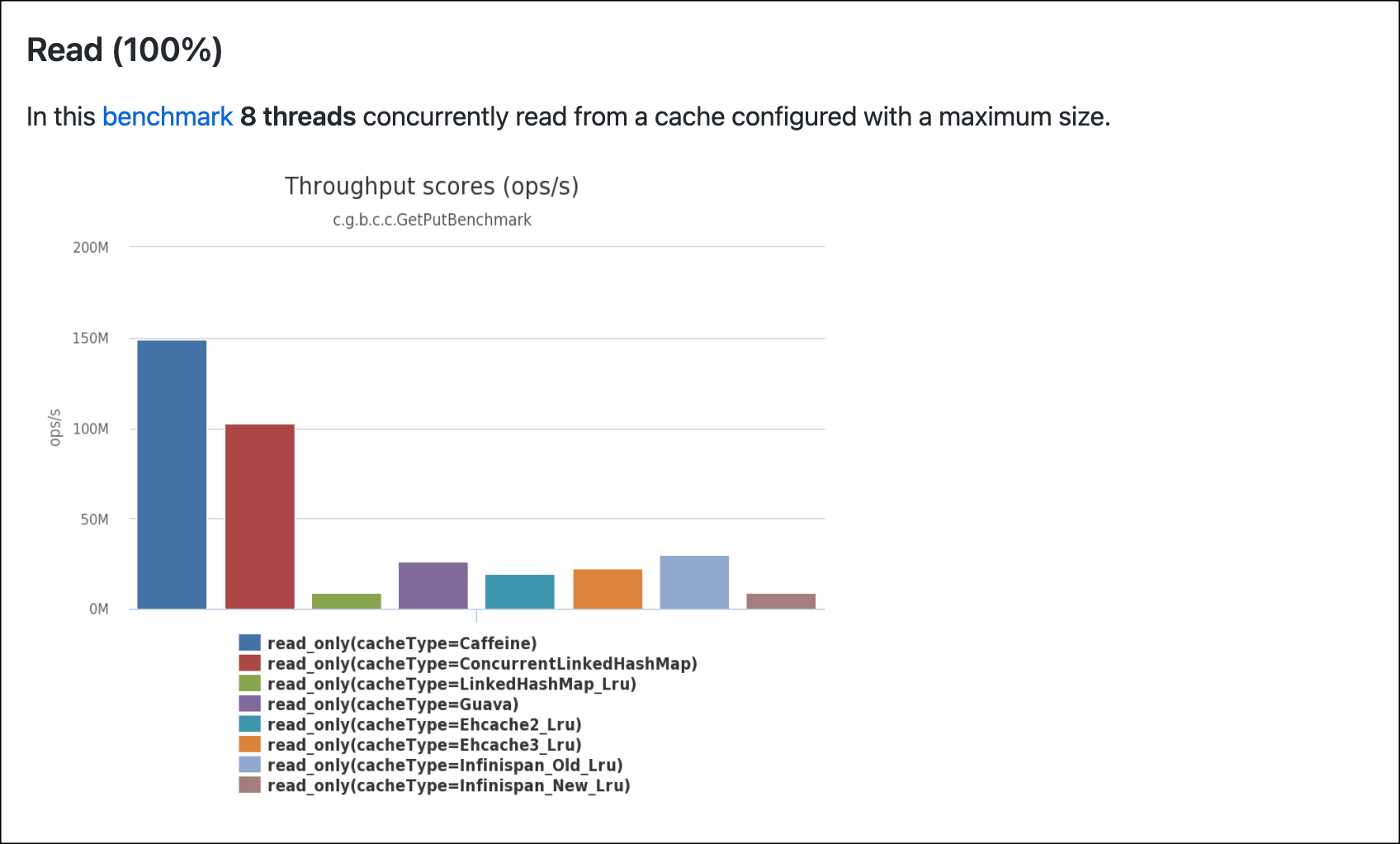
읽기 100% 성능 측정 테스트에서는 Caffeine Cache 가 가장 좋은 성능을 보여주었고 그 다음으로는 ConcurrentLinkedHashMap 이 좋은 성능을 보여주었다.
위에서 비교했던 EhCache 는 다소 아쉬운 성능을 보여주었다.
읽기 75% 쓰기 25% 성능 측정
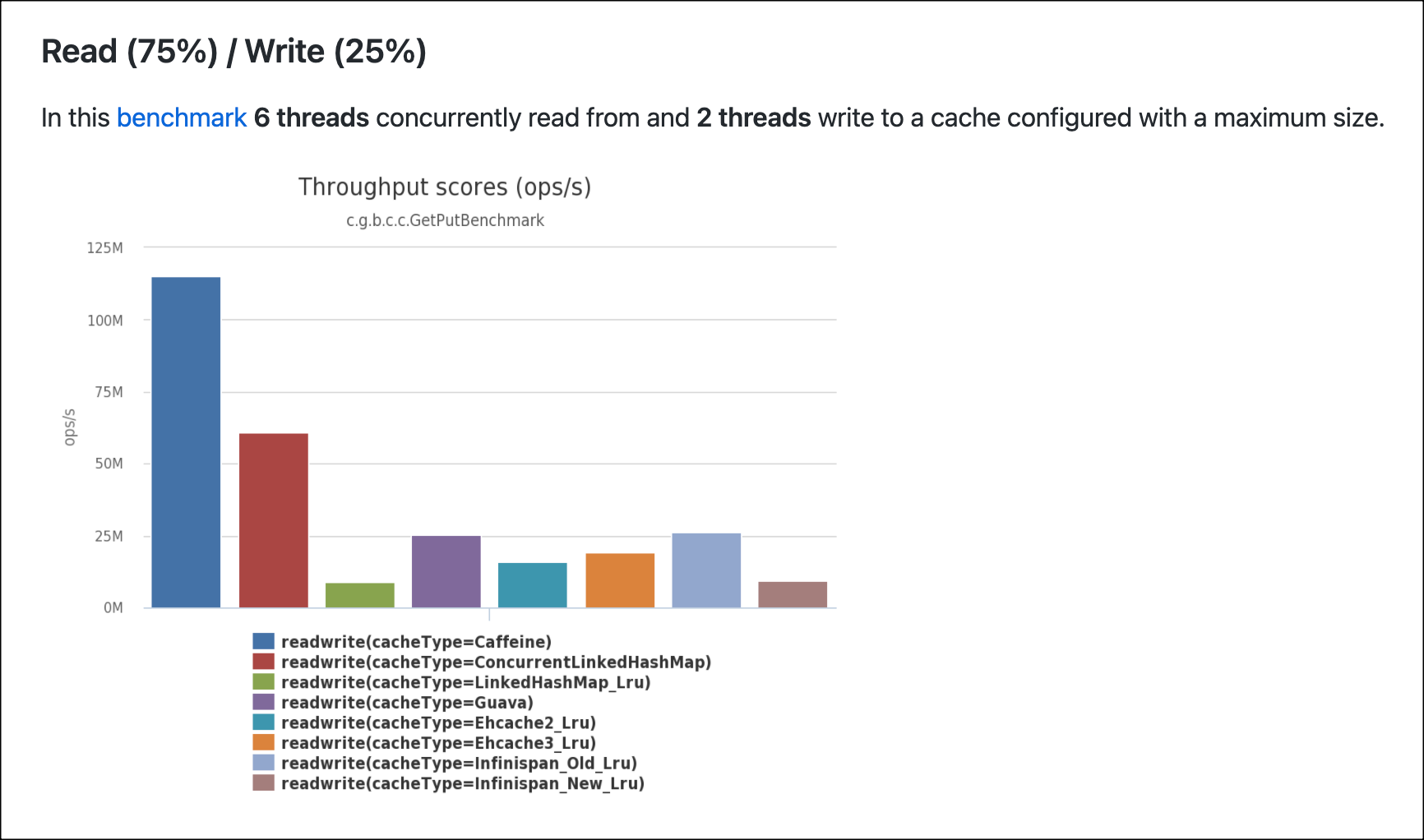
읽기 75% 쓰기 25% 성능 측정 테스트에서도 역시 Caffeine Cache 가 가장 좋은 성능을 보여주었고 그 다음으로는 ConcurrentLinkedHashMap 이 좋은 성능을 보여주었다.
하지만, 읽기 100% 성능 측정과는 다르게 Caffeine Cache 와 ConcurrentLinkedHashMap 의 성능 차이가 2배 정도 차이가 나는 것을 볼 수 있다.
마찬가지로 위에서 비교했던 EhCache 는 다소 아쉬운 성능을 보여주었다.
쓰기 100% 성능 측정
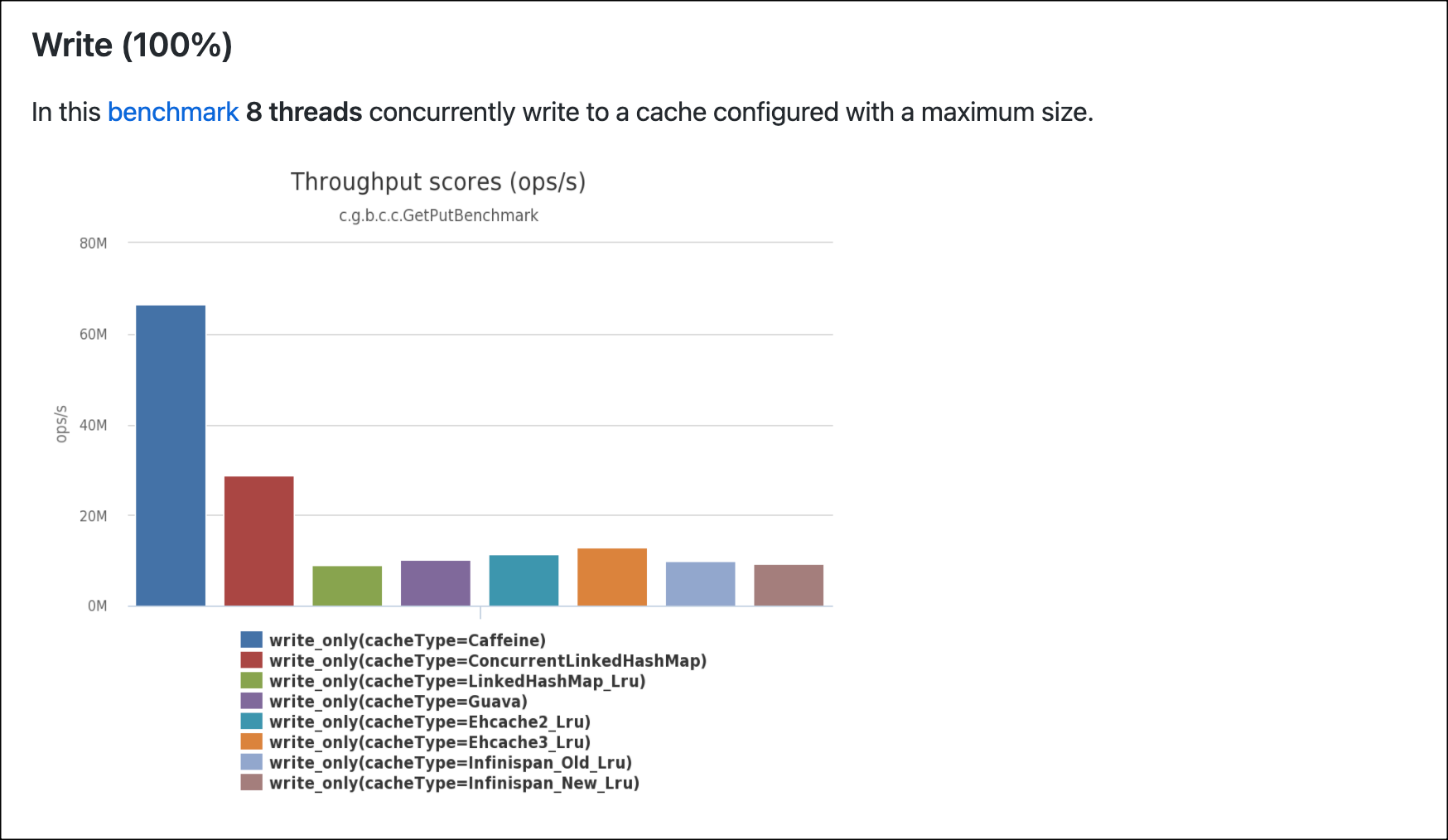
쓰기 100% 성능 측정 테스트에서도 역시 Caffeine Cache 가 가장 좋은 성능을 보여주었고 그 다음으로는 ConcurrentLinkedHashMap 이 좋은 성능을 보여주었다.
마찬가지로 Caffeine Cache 와 ConcurrentLinkedHashMap 의 성능 차이가 2배 정도 차이가 나는 것을 볼 수 있다.
정리하자면, Caffeine Cache 는 EhCache 처럼 다양한 기능은 제공하지는 않지만 심플하게 메모리에 데이터를 캐싱하고 불러오는 작업만 한다면 가장 뛰어난 성능을 보여준다.
Caffeine cache example
이제 Spring boot 환경에서 사용 예시를 간단하게 살펴보자
Caffeine cahce 를 사용하기 위해 아래와 같이 의존성을 추가하자.
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-cache'
implementation 'com.github.ben-manes.caffeine:caffeine'
}
그 다음 @EnableCaching 를 사용하여 스프링 어플리케이션이 캐시를 사용할 수 있게 하자.
@EnableCaching // 캐시 기능을 활성화한다.
@SpringBootApplication
public class CacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
이제 캐시에 대한 Enum 값을 정의하자.
@Getter
public enum CacheType {
USERS(
"users", // 캐시 이름: users
5 * 60, // 만료 시간: 5 분
10000 // 최대 갯수: 10000
);
CacheType(String cacheName, int expireAfterWrite, int maximumSize) {
this.cacheName = cacheName;
this.expireAfterWrite = expireAfterWrite;
this.maximumSize = maximumSize;
}
private final String cacheName;
private final int expireAfterWrite;
private final int maximumSize;
}Enum 을 사용하여 캐시 이름, 만료 시간, 저장 가능한 최대 갯수를 정의하였다.
그 다음, cacheManager 를 Bean 으로 등록하자.
@Configuration
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager() {
List<CaffeineCache> caches = Arrays.stream(CacheType.values())
.map(cache -> new CaffeineCache(cache.getCacheName(), Caffeine.newBuilder().recordStats()
.expireAfterWrite(cache.getExpireAfterWrite(), TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.maximumSize(cache.getMaximumSize())
.build()
)
)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
SimpleCacheManager cacheManager = new SimpleCacheManager();
cacheManager.setCaches(caches);
return cacheManager;
}
}CacheType 에 등록한 캐시들을 Caffeine 캐시 객체로 생성 후 SimpleCacheManager 객체에 등록하였다.
이제 캐시가 정상적으로 동작하는지 아래 유저 객체를 사용하여 테스트를 해보자.
@Getter
public class User {
private final Long id;
private final String email;
private final String name;
@Builder
public User(Long id, String email, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.email = email;
this.name = name;
}
}
테스트를 위해 간단한 Controller 를 작성해보았다.
@RestController
public class UserController {
Map<Long, User> userMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
User user1 = User.builder()
.id(1L)
.name("test1")
.email("test1@test.com")
.build();
User user2 = User.builder()
.id(2L)
.name("test2")
.email("test2@test.com")
.build();
User user3 = User.builder()
.id(3L)
.name("test3")
.email("test3@test.com")
.build();
userMap.put(user1.getId(), user1);
userMap.put(user2.getId(), user2);
userMap.put(user3.getId(), user3);
}
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "users")
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User> getUser() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(10000);
Set<Long> userIds = userMap.keySet();
return userIds.stream()
.map(userId -> userMap.get(userId))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}간단하게 코드를 작성하기 위해서 Controller, Service, Repository 로 계층을 구분하지 않고 1 Layer 로 작성하였다.
데이터는 DB 는 사용하지 않고 간단하게 ConcurrentHashMap 을 사용하여 어플리케이션이 실행될 때 초기화를 하도록 만들었다.
그리고 성능 측정을 위하여 GET /users 가 호출되면 10s 동안 thread 를 sleep 하도록 api 를 만들었다.
이제 api 호출을 통해 캐시가 정상적으로 동작하는지 살펴보자.
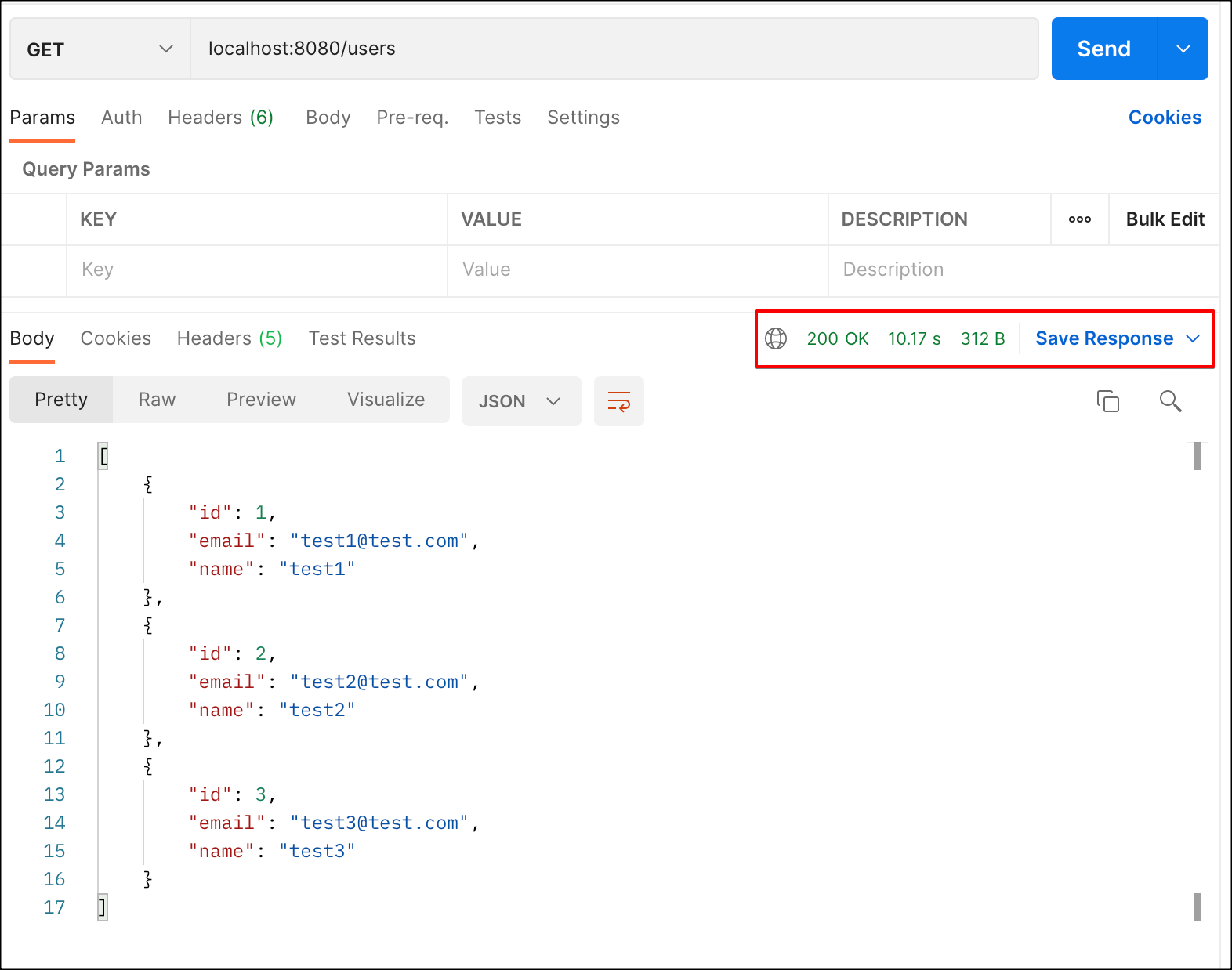
첫 번째 호출할 때는 응답 시간이 약 10s 정도 걸린 것을 볼 수 있다.
다시 한 번 api 를 호출해보자.
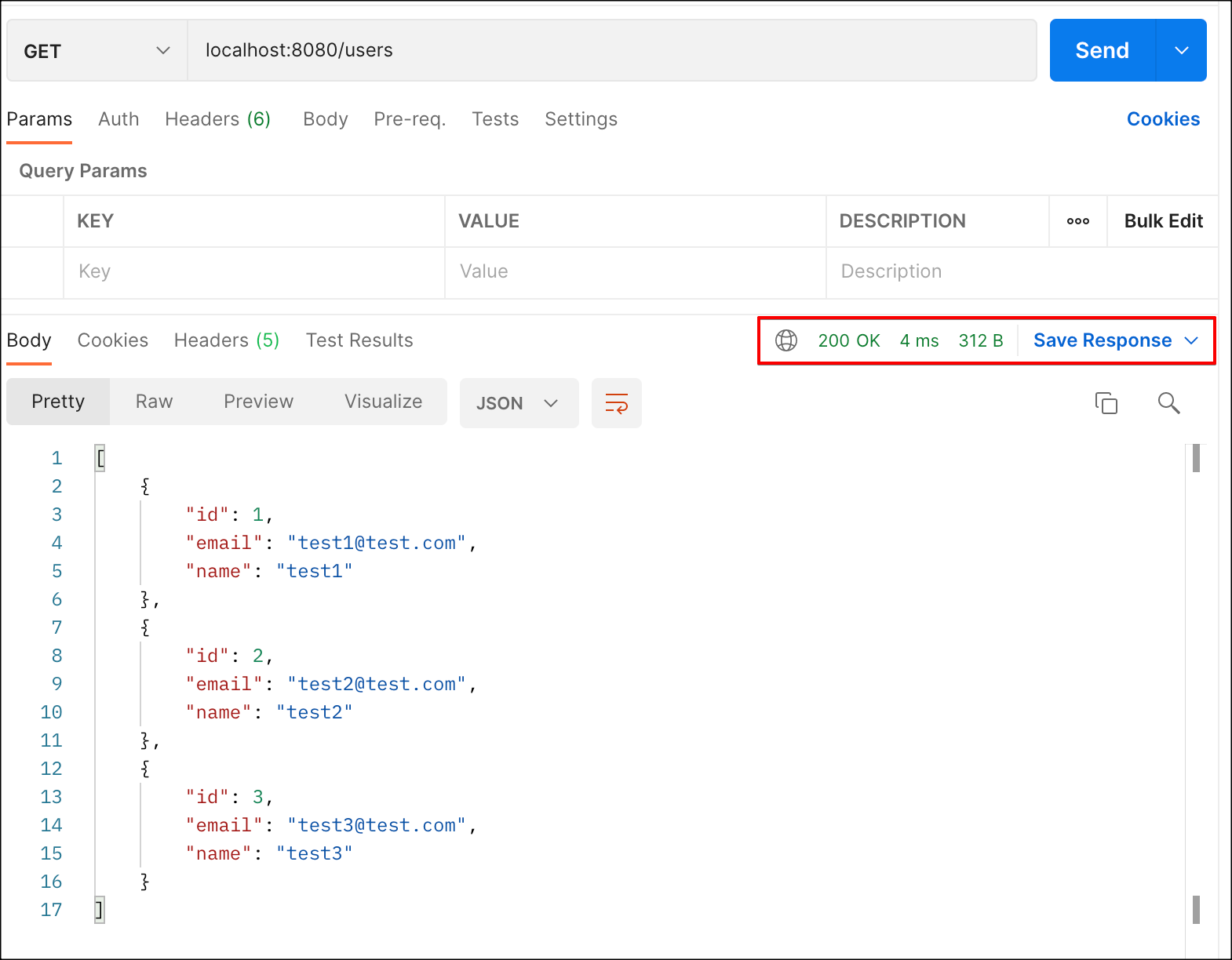
두 번째 호출부터 약 4ms 정도 걸리는 것을 볼 수 있다.
참고
https://github.com/ben-manes/caffeine/wiki
GitHub - ben-manes/caffeine: A high performance caching library for Java
A high performance caching library for Java. Contribute to ben-manes/caffeine development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
https://www.ehcache.org/documentation/3.4/tiering.html
Ehcache Tiering Options
In order to understand what happens for different cache operations when using multiple tiers, here are examples of Put and Get operations. The sequence diagrams are oversimplified but still show the main points. Figure 2. Multiple tiers using Put Figure 3.
www.ehcache.org
https://gosunaina.medium.com/cache-redis-ehcache-or-caffeine-45b383ae85ee
Cache — Redis, EhCache or Caffeine?
A cache is a reserved storage location that collects temporary data to help websites, browsers, and apps load faster. The data stored in a…
gosunaina.medium.com
https://blog.yevgnenll.me/posts/spring-boot-with-caffeine-cache
Spring boot 에 caffeine 캐시를 적용해보자 - 어떻게하면 일을 안 할까?
부제: 어떻게 하면 일을 조금이라도 안할까?
blog.yevgnenll.me
'Spring Framework > 개념' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring Data :: Spring Data Elasticsearch rollover index 정리 (1) | 2021.11.26 |
|---|---|
| Spring Cloud :: Spring cloud sleuth 정리 (0) | 2021.11.13 |
| Spring boot :: Multiple DataSource 환경에서 @DataJpaTest 이슈 정리 및 스프링 코드 분석 (4) | 2021.10.11 |
| Spring boot :: Mockito 로 WebClient 테스트 하기 (1) | 2021.09.26 |
| Spring boot :: JPA, Mybatis Transaction Manager 정리 (1) | 2021.09.06 |




